最近在深入学习 Kubernetes 基础知识,通过追踪 HTTP 请求到达 Kubernetes 集群上的服务过程来深入学习 Kubernetes 实现原理。希望下列文章能够对我们熟悉 Kubernetes 有一定的帮助。
- Linux 网络、Namespace 与容器网络 CNI 基础知识
- Kubernetes CNI 大利器 - Calico
- Kubernetes 流量核心组件 - kube-proxy
- Kubernetes 使用 Ingress 处理七层流量
Linux 命名空间(Linux Namespaces)
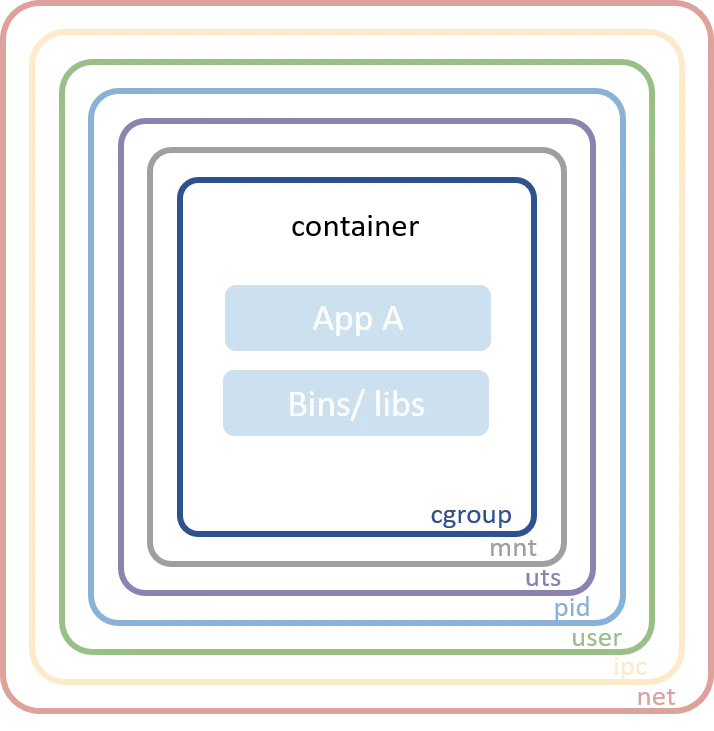
Linux 命名空间是大多数现代容器实现背后的技术。它们允许独立进程之间隔离全局系统资源。例如,PID命名空间隔离了进程ID命名空间,在同一主机上运行的两个进程可以拥有相同的PID。 在容器的世界中,这种隔离级别显然是非常有用的。没有命名空间,容器A中运行的进程可以卸载容器B中的重要文件系统,或者更改容器C的主机名,或者从容器D中移除网络接口。通过对这些资源进行命名空间化,容器A中的进程甚至无法意识到容器B、C和D中的进程存在。Linux 内核中常见的命令空间如下所示:
- Mount - 隔离文件系统挂载点
- UTS - 隔离主机名和域名
- IPC - 隔离进程间通信(IPC)资源
- PID - 隔离PID命名空间
- Network - 隔离网络接口
- User - 隔离UID/GID命名空间
- Cgroup - 隔离cgroup根目录
更多有关 Linux Namespace 详情可参考 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linux_namespaces#Namespace_kinds
容器网络(Network Namespace)
在深入理解CNI之前,我们先熟悉网络命名空间。让我们使用 ip 命令创建两个不同的网络命名空间,并将它们分别命名为客户端 client 和服务器 server。
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns add client
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns add server
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns list
server
client
上述内容创建完成后,我们其实可以在 /run/netns 目录下看见该文件,如下所示:
root@instance-frllxehj:/run/netns# pwd
/run/netns
创建一个 veth 对来连接这些网络命名空间。
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip link list | grep veth
3: veth-server@veth-client: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,M-DOWN> mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
4: veth-client@veth-server: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,M-DOWN> mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
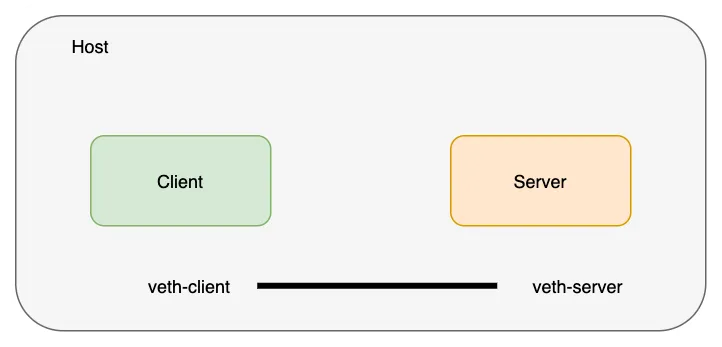
veth对(网络线)存在于主机网络命名空间中;我们将 veth 对的两端移动到我们之前创建的各自的命名空间中。注意:主机网络命名空间是看不到 veth 对的。
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip link set veth-client netns client
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip link set veth-server netns server
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip link list | grep veth
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen#
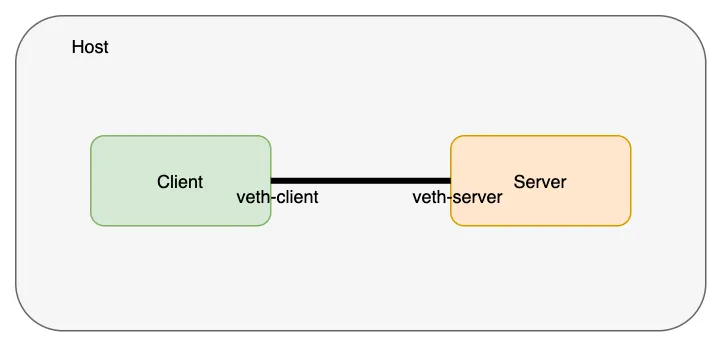
让我们验证veth的两端是否真的存在于这些命名空间中。
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns exec client ip link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK> mtu 65536 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
4: veth-client@if3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether ba:15:14:e4:04:79 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netns server
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns exec server ip link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK> mtu 65536 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
3: veth-server@if4: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 46:7d:31:fe:e9:bd brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netns client
现在让我们给这些接口分配IP地址并启动它们。
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns exec client ip address add 10.0.0.11/24 dev veth-client
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns exec client ip link set veth-client up
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns exec server ip address add 10.0.0.12/24 dev veth-server
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns exec server ip link set veth-server up
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns exec client ip addr
1: lo: <LOOPBACK> mtu 65536 qdisc noop state DOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
4: veth-client@if3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether ba:15:14:e4:04:79 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netns server
inet 10.0.0.11/24 scope global veth-client
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::b815:14ff:fee4:479/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns exec server ip addr
1: lo: <LOOPBACK> mtu 65536 qdisc noop state DOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
3: veth-server@if4: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 46:7d:31:fe:e9:bd brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netns client
inet 10.0.0.12/24 scope global veth-server
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::447d:31ff:fefe:e9bd/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
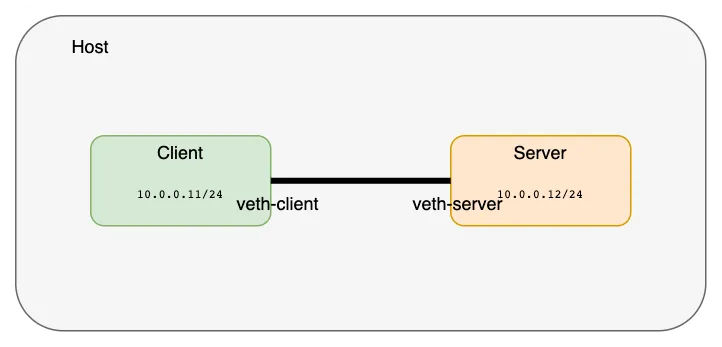
使用 ping 命令验证这两个网络命名空间已经被连接并且是可达的。
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns exec client ping 10.0.0.12
PING 10.0.0.12 (10.0.0.12) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.0.0.12: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.037 ms
64 bytes from 10.0.0.12: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.020 ms
^C
--- 10.0.0.12 ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1010ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.020/0.028/0.037/0.008 ms
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns exec server ping 10.0.0.11
PING 10.0.0.11 (10.0.0.11) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.0.0.11: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.018 ms
64 bytes from 10.0.0.11: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.017 ms
^C
--- 10.0.0.11 ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1019ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.017/0.017/0.018/0.000 ms
注意:执行以下操作删除上述创建的网络命名空间。
# 删除设置的IP地址
ip netns exec server ip address del 10.0.0.12/24 dev veth-server
ip netns exec client ip address del 10.0.0.11/24 dev veth-client
# 将网络接口移出网络命名空间
ip link set veth-server netns 1
ip link set veth-client netns 1
# 删除网络命名空间
ip netns del server
ip netns del client
如果想要创建更多的网络命名空间并将它们连接在一起,为每一对命名空间创建一个veth对不是一个可扩展的解决方案。 我们可以创建一个Linux桥接,并将这些网络命名空间连接到网桥上以获取连接性。这正是Docker在同一主机上运行的容器之间设置网络的方式。 让我们使用以下脚本创建命名空间并将其连接到网桥上测试 Docker 默认桥接模式。
HOST_IP=192.168.0.7
BR=bridge1
ip link add client1-veth type veth peer name client1-veth-br
ip link add server1-veth type veth peer name server1-veth-br
ip link add $BR type bridge
ip netns add client1
ip netns add server1
ip link set client1-veth netns client1
ip link set server1-veth netns server1
ip link set client1-veth-br master $BR
ip link set server1-veth-br master $BR
ip link set $BR up
ip link set client1-veth-br up
ip link set server1-veth-br up
ip netns exec client1 ip link set client1-veth up
ip netns exec server1 ip link set server1-veth up
ip netns exec client1 ip addr add 172.30.0.11/24 dev client1-veth
ip netns exec server1 ip addr add 172.30.0.12/24 dev server1-veth
ip addr add 172.30.0.1/24 dev $BR
ip netns exec client1 ping 172.30.0.12 -c 5
ip netns exec client1 ping 172.30.0.1 -c 5
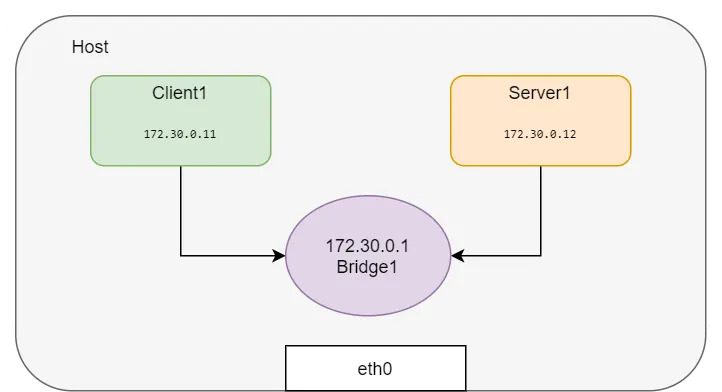
使用 ping 命令,我们可以验证两个网络命名空间已连接并且可以互相访问。
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns exec client1 ping 172.30.0.1 -c 5
PING 172.30.0.1 (172.30.0.1) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 172.30.0.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.040 ms
64 bytes from 172.30.0.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.037 ms
^C
--- 172.30.0.1 ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1025ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.037/0.038/0.040/0.001 ms
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns exec server1 ping 172.30.0.1 -c 5
PING 172.30.0.1 (172.30.0.1) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 172.30.0.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.062 ms
64 bytes from 172.30.0.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.032 ms
64 bytes from 172.30.0.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.036 ms
从命名空间 ping 主机IP,出现“网络不可达”,因为在新创建的命名空间中尚未配置路由。让我们添加默认路由:
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns exec client1 ping $HOST_IP -c 2
ping: connect: Network is unreachable
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns exec server1 ping $HOST_IP -c 2
ping: connect: Network is unreachable
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns exec client1 ip route show
172.30.0.0/24 dev client1-veth proto kernel scope link src 172.30.0.11
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns exec server1 ip route show
172.30.0.0/24 dev server1-veth proto kernel scope link src 172.30.0.12
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns exec client1 ip route add default via 172.30.0.1
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns exec server1 ip route add default via 172.30.0.1
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns exec server1 ip route show
default via 172.30.0.1 dev server1-veth
172.30.0.0/24 dev server1-veth proto kernel scope link src 172.30.0.12
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns exec client1 ip route show
default via 172.30.0.1 dev client1-veth
172.30.0.0/24 dev client1-veth proto kernel scope link src 172.30.0.11
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ip netns exec client1 ping $HOST_IP -c 5
PING 192.168.0.7 (192.168.0.7) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.0.7: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.040 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.7: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.043 ms
现在,访问外部网络的“默认”路由是桥接模式,因此命名空间可以使用任何外部网络服务,如下所示:
root@instance-frllxehj:~/tanjunchen# ping 8.8.8.8 -c 2
PING 8.8.8.8 (8.8.8.8) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 8.8.8.8: icmp_seq=1 ttl=53 time=1.51 ms
64 bytes from 8.8.8.8: icmp_seq=2 ttl=53 time=1.44 ms
备注:我们可以通过以下手段删除上述常见的网络设备。
ip link del client1-veth-br
ip link del server1-veth-br
ip netns exec client1 ip link del client1-veth
ip netns exec server1 ip link del server1-veth
ip netns del client1
ip netns del server1
BR=bridge1
ip link del $BR
如何从外部服务器访问私有网络?
在网络命名空间(Namespace)上下文中运行 Web 服务器并不容易,因为所有的 Linux 命名空间需要协同工作才能模拟这种场景。为简化操作,我们可以利用 Docker 来模拟这一场景。
让我们启动一个 Nginx 容器,并检查相关信息:
root@instance-70s5fat5:~# docker run -d --name web --rm nginx
Unable to find image 'nginx:latest' locally
latest: Pulling from library/nginx
fd674058ff8f: Downloading [===========================> ] 15.29MB/28.23MB
fd674058ff8f: Downloading [===========================> ] 15.59MB/28.23MB
2b99b9c5d9e5: Download complete
fd674058ff8f: Pull complete
566e42bcee1c: Pull complete
2b99b9c5d9e5: Pull complete
bd98674871f5: Pull complete
1e109dd2a0d7: Pull complete
da8cc133ff82: Pull complete
c44f27309ea1: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:42e917aaa1b5bb40dd0f6f7f4f857490ac7747d7ef73b391c774a41a8b994f15
Status: Downloaded newer image for nginx:latest
e09ffc5b9c8fbeea229ea4676b766c201d246e114a14d4e2de08aae90a5a5dd8
获取容器的 IP 地址与检查容器的网络命名空间路径:
root@instance-70s5fat5:~# WEB_IP=`docker inspect -f "{{ .NetworkSettings.IPAddress }}" web`
root@instance-70s5fat5:~# docker inspect web --format '{{ .NetworkSettings.SandboxKey }}'
/var/run/docker/netns/0d2b6c023fe9
root@instance-70s5fat5:~# ip netns list
server1 (id: 1)
client1 (id: 0)
Docker 不会在默认位置创建网络命名空间,因此 ip netns list 无法显示该命名空间,通过创建符号链接来解决此问题:
controlplane $ container_id=web
controlplane $ container_netns=$(docker inspect ${container_id} --format '{{ .NetworkSettings.SandboxKey }}')
controlplane $ mkdir -p /var/run/netns
controlplane $ rm -f /var/run/netns/${container_id}
controlplane $ ln -sv ${container_netns} /var/run/netns/${container_id}
'/var/run/netns/web' -> '/var/run/docker/netns/c009f2a4be71'
验证网络命名空间是否已列出:
root@instance-70s5fat5:/var/run/netns# ll
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 100 Jan 1 14:25 ./
drwxr-xr-x 28 root root 1020 Jan 1 14:02 ../
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 1 14:02 client1
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 1 14:02 server1
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 34 Jan 1 14:24 web -> /var/run/docker/netns/0d2b6c023fe9
root@instance-70s5fat5:/var/run/netns# ip netns list
web (id: 2)
server1 (id: 1)
client1 (id: 0)
在命名空间中查看 IP 地址:
root@instance-70s5fat5:/var/run/netns# ip netns exec web ip addr
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
9: eth0@if10: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether 02:42:ac:11:00:02 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet 172.17.0.2/16 brd 172.17.255.255 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
root@instance-70s5fat5:/var/run/netns# echo $WEB_IP
172.17.0.2
容器通过 Linux 命名空间实现了完全隔离,我们可以从主机访问运行在容器内的 Web 应用:
root@instance-70s5fat5:/var/run/netns# curl $WEB_IP
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
html { color-scheme: light dark; }
body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto;
font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
<p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
working. Further configuration is required.</p>
<p>For online documentation and support please refer to
<a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/>
Commercial support is available at
<a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p>
<p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p>
</body>
</html>
CNI 插件执行了上述命令(不完全相同,但类似)来配置回环接口、eth0 并为容器分配 IP 地址。我们将在下一节讨论 CNI。
什么是 CNI?
CNI 插件负责将网络接口插入到容器网络命名空间中(例如,veth对的一端),并在主机上进行必要的更改(例如,将veth的另一端连接到一个桥)。他将IP分配给网络接口,并通过调用IPAM插件设置与IP地址管理部分一致的路由。CNI仅关注容器的网络连接以及在删除容器时移除分配的资源。
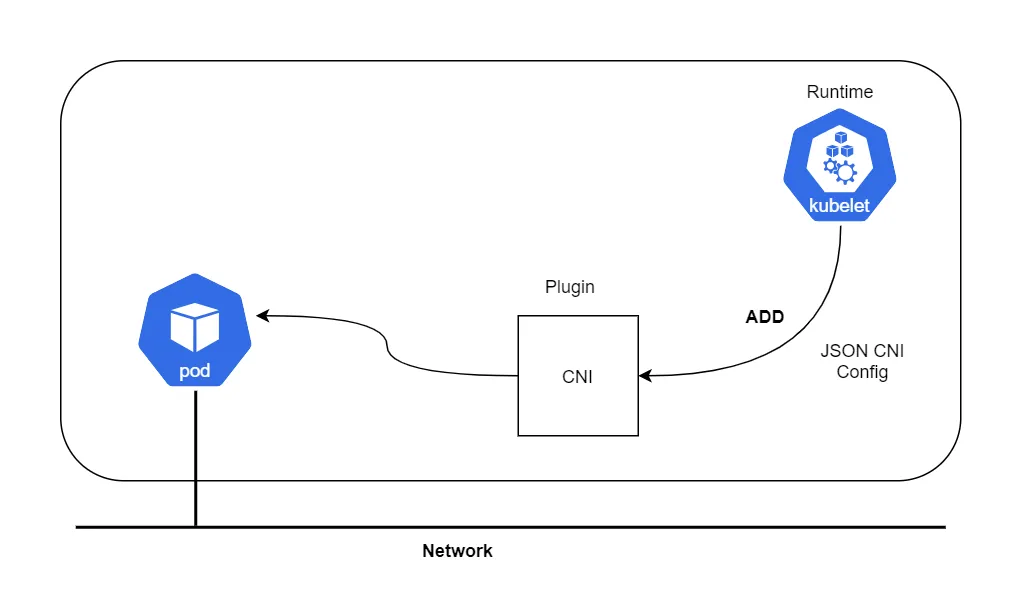
Runtime 运行时可以是任何东西 - 例如 Kubernetes、PodMan、Cloud Foundry等。
CNI 规范
CNI 规范可参考 https://github.com/containernetworking/cni/blob/master/SPEC.md,CNI 具体特征如下所示:
- 该规范将容器定义为Linux网络命名空间,像Docker这样的容器运行时为每个容器创建一个新的网络命名空间
- CNI的网络定义存储为JSON文件
- 网络定义通过STDIN流向插件,主机上没有网络配置的配置文件
- 其他参数通过环境变量传递给插件
- CNI插件是作为一个可执行程序实现的
- CNI插件负责容器连接,它需要做所有的工作使容器可以连接到网络
- CNI插件负责IPAM,包括IP地址分配和配置所需的路由
接下来手动模拟Pod的创建,不通过Kubernetes与CNI插件分配IP,而是使用CLI命令。演示完这个示例后,我们将深入理解 Kubernetes 中的 Pod CNI 容器网络。
- 下载 CNI 插件
root@instance-70s5fat5:~/cni# wget https://github.com/containernetworking/cni/releases/download/v0.5.0/cni-amd64-v0.5.0.tgz
root@instance-70s5fat5:~/cni# tar -xvf cni-amd64-v0.5.0.tgz
./
./macvlan
./dhcp
./loopback
./ptp
./ipvlan
./bridge
./tuning
./noop
./host-local
./cnitool
./flannel
2.创建 CNI JSON 配置文件
cat > /tmp/00-demo.conf <<"EOF"
{
"cniVersion": "0.3.0",
"name": "demo_br",
"type": "bridge",
"bridge": "cni_net0",
"isGateway": true,
"ipMasq": true,
"ipam": {
"type": "host-local",
"subnet": "10.0.10.0/24",
"routes": [
{ "dst": "0.0.0.0/0" },
{ "dst": "1.1.1.1/32", "gw":"10.0.10.1"}
]
}
}
EOF
3.创建一个网络模式为 none 的容器,这样该容器将不会有任何可用的 IP 地址。
root@instance-70s5fat5:~/cni# docker run --name pause_demo -d --rm --network none k8s.gcr.io/pause:3.9
Unable to find image 'k8s.gcr.io/pause:3.9' locally
3.9: Pulling from pause
61fec91190a0: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:7031c1b283388d2c2e09b57badb803c05ebed362dc88d84b480cc47f72a21097
Status: Downloaded newer image for k8s.gcr.io/pause:3.9
16395083935b4e5e77dd95342e0e31678e5a4e65a872ca93a791da49291c55b1
root@instance-70s5fat5:~/cni# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
16395083935b k8s.gcr.io/pause:3.9 "/pause" 12 seconds ago Up 11 seconds pause_demo
root@instance-70s5fat5:~/cni# container_id=pause_demo
root@instance-70s5fat5:~/cni# container_netns=$(docker inspect ${container_id} --format '{{ .NetworkSettings.SandboxKey }}')
root@instance-70s5fat5:~/cni# echo $container_id
pause_demo
root@instance-70s5fat5:~/cni# echo $container_netns
/var/run/docker/netns/47bcefca9939
root@instance-70s5fat5:~/cni# mkdir -p /var/run/netns
root@instance-70s5fat5:~/cni# rm -f /var/run/netns/${container_id}
root@instance-70s5fat5:~/cni# ln -sv ${container_netns} /var/run/netns/${container_id}
'/var/run/netns/pause_demo' -> '/var/run/docker/netns/47bcefca9939'
root@instance-70s5fat5:~/cni# ip netns list
pause_demo
web
root@instance-70s5fat5:~/cni# ip netns exec $container_id ifconfig
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host>
loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
4.使用 CNI 配置文件调用 CNI 插件
root@instance-70s5fat5:~/cni# CNI_CONTAINERID=$container_id CNI_IFNAME=eth10 CNI_COMMAND=ADD CNI_NETNS=/var/run/netns/$container_id CNI_PATH=`pwd` ./bridge </tmp/00-demo.conf
{
"interfaces": [
{
"name": "cni_net0",
"mac": "0a:58:0a:00:0a:01"
},
{
"name": "veth61683440",
"mac": "ca:7b:bc:fc:73:f4"
},
{
"name": "eth10",
"mac": "0a:58:0a:00:0a:02",
"sandbox": "/var/run/netns/pause_demo"
}
],
"ips": [
{
"version": "4",
"interface": 2,
"address": "10.0.10.2/24",
"gateway": "10.0.10.1"
}
],
"routes": [
{
"dst": "0.0.0.0/0"
},
{
"dst": "1.1.1.1/32",
"gw": "10.0.10.1"
}
],
"dns": {}
}
更多详细信息可以阅读 CNI 规范,比如可以在同一个 JSON 文件中使用多个插件来链式执行操作,例如添加防火墙规则等。
5.CNI 会根据配置文件创建一个网桥并进行相应的配置
root@instance-70s5fat5:~/cni# ip netns exec pause_demo ifconfig
eth10: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 10.0.10.2 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 0.0.0.0
inet6 fe80::4432:8ff:fef6:53a6 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 0a:58:0a:00:0a:02 txqueuelen 0 (Ethernet)
RX packets 37 bytes 2883 (2.8 KB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 20 bytes 2281 (2.2 KB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host>
loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
root@instance-70s5fat5:~/cni# ip netns exec pause_demo ip route
default via 10.0.10.1 dev eth10
1.1.1.1 via 10.0.10.1 dev eth10
10.0.10.0/24 dev eth10 proto kernel scope link src 10.0.10.2
root@instance-70s5fat5:~/cni# ifconfig
cni_net0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 10.0.10.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 0.0.0.0
inet6 fe80::2452:25ff:fee1:f8d2 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 0a:58:0a:00:0a:01 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 20 bytes 2001 (2.0 KB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 26 bytes 2041 (2.0 KB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
6.启动一个 Web 服务器并共享 pause 容器的命名空间
root@instance-70s5fat5:~/cni# docker run --name web_demo -d --rm --network container:$container_id nginx
f045b0da9253c8a84170ae36f7542287cad813de522363cc1c156bf526742cd7
root@instance-70s5fat5:~/cni# curl `cat /var/lib/cni/networks/demo_br/last_reserved_ip`
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
html { color-scheme: light dark; }
body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto;
7.要使用 pause 容器的 IP 地址浏览 nginx
root@instance-70s5fat5:~/cni# curl `cat /var/lib/cni/networks/demo_br/last_reserved_ip`
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
html { color-scheme: light dark; }
body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto;
font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
<p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
working. Further configuration is required.</p>
<p>For online documentation and support please refer to
<a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/>
Commercial support is available at
<a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p>
<p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p>
</body>
</html>
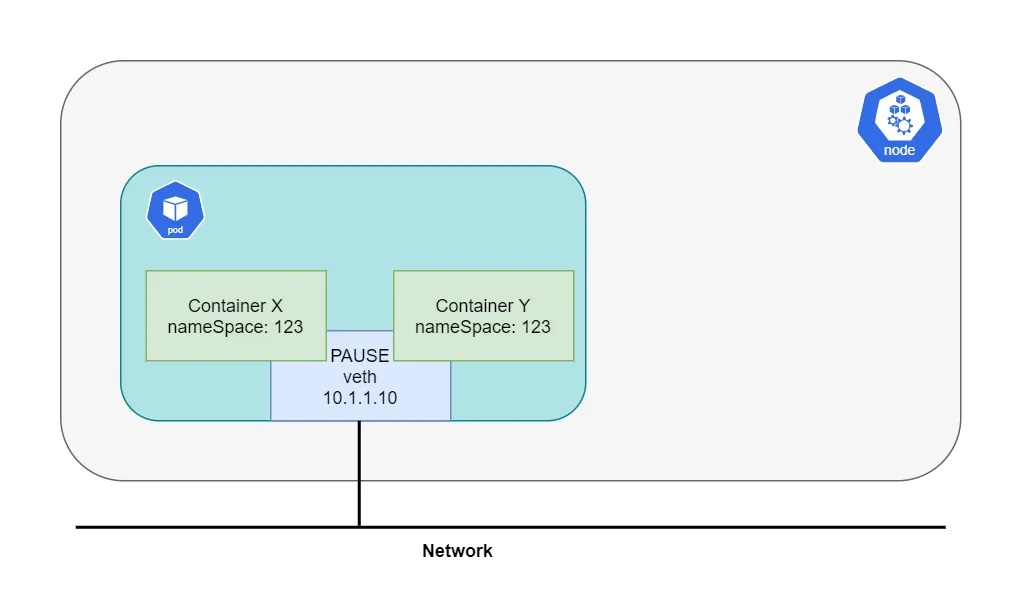
总结:在 Kubernetes 中,首先需要理解的是,POD 并不完全等同于一个容器,而是一个容器的集合。而属于同一个 POD 的所有容器共享一个网络栈。Kubernetes 通过在每个 POD 中创建的 pause 容器来管理网络。对于创建的每个 POD,都可以找到一个 pause 容器。 其他容器都会附加到 pause 容器的网络上,而 pause 容器本身的作用仅仅是提供网络支持。因此,同一个 POD 中的容器可以通过 localhost 与其他容器之间进行通信。这种网络共享机制是 Kubernetes 的核心功能之一。如下图所示: