Scheduler 分两个 cycle:Scheduling Cycle 和 Binding Cycle。在 Scheduling Cycle 中为了提升效率的一个重要原则就是 Pod、 Node 等信息从本地缓存中获取,而具体的实现原理就是先使用 list 获取所有 Node、Pod 的信息,然后再 watch 他们的变化更新本地缓存。在 Bind Cycle 中,会有两次外部 api 调用:调用 pv controller 绑定 pv 和调用 kube-apiserver 绑定 Node,api 调用是耗时的,所以将 bind 扩展点拆分出来,另起一个 go 协程进行 bind。调度周期是串行,绑定周期是并行的。本文主要介绍 Scheduler Framework 框架整体架构与 Pod 调度到 Node 流程插件拓展点。
深入理解 Kubernetes Scheduler Framework 调度框架(Part 4)
深入理解 Kubernetes Scheduler Framework 调度框架(Part 3)
深入理解 Kubernetes Scheduler Framework 调度框架(Part 2)
深入理解 Kubernetes Scheduler Framework 调度框架(Part 1)
调度器介绍
Kubernetes 官方对于 scheduler 调度器的解释如下所示:
The Kubernetes scheduler is a control plane process which assigns Pods to Nodes.
The scheduler determines which Nodes are valid placements for each Pod in the scheduling queue
according to constraints and available resources.
The scheduler then ranks each valid Node and binds the Pod to a suitable Node.
Multiple different schedulers may be used within a cluster.
kube-scheduler is the reference implementation.
Pod 调度到 Node 上,Kubernetes 各个组件交互流程如下所示:
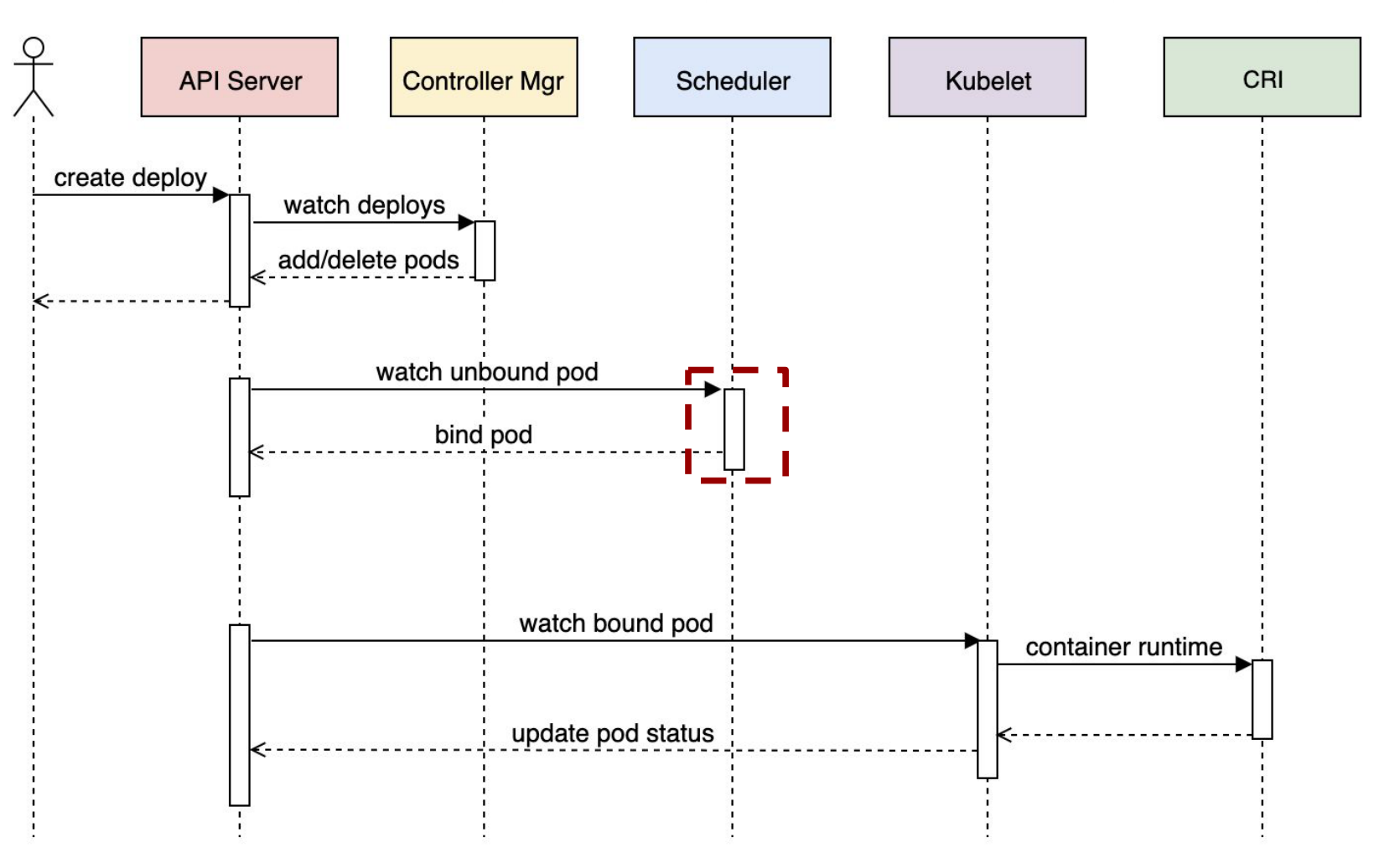
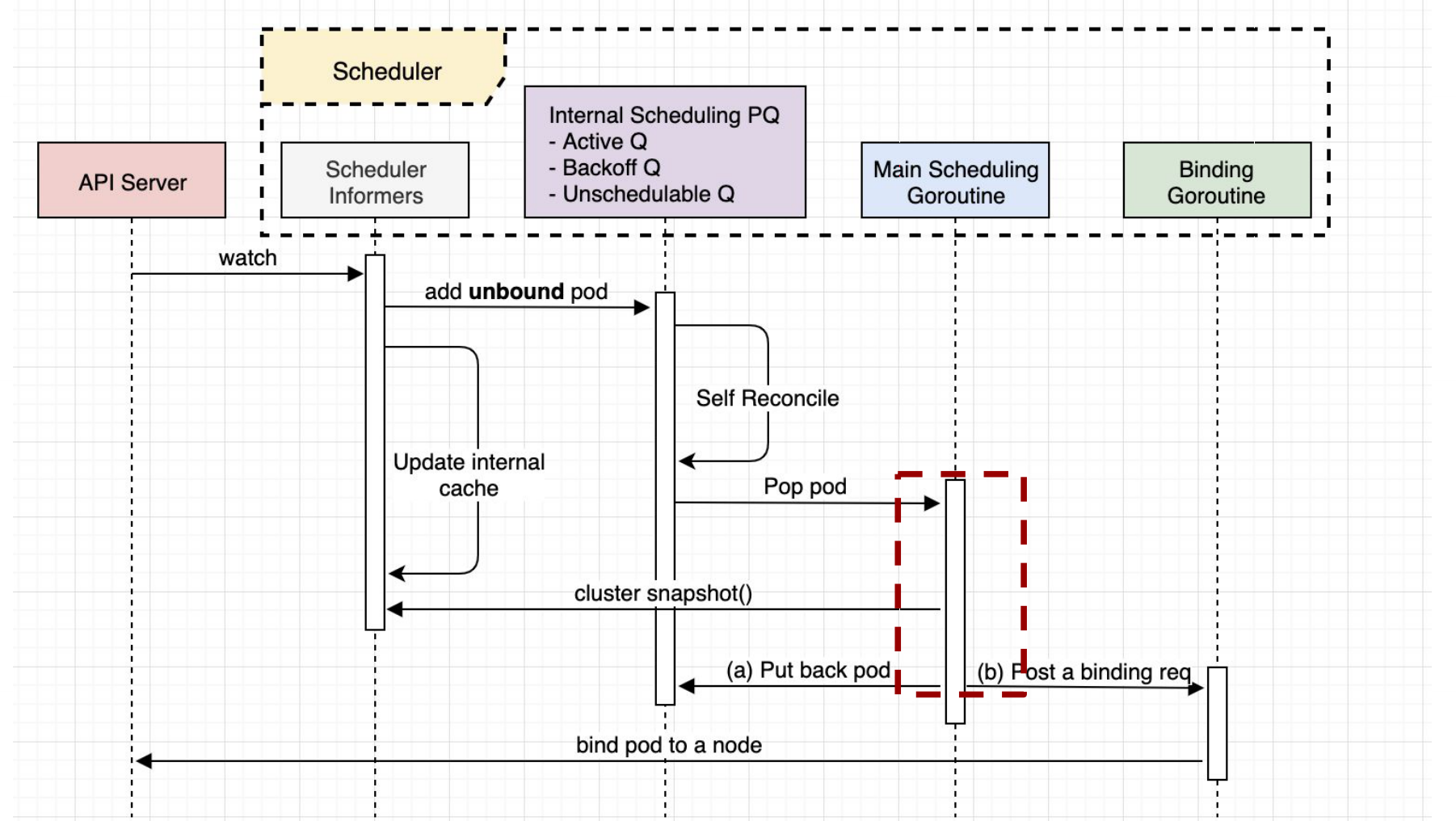
Pod 调度到 Node 上,Kubernetes Scheduler 的核心流程如下所示:
基于预选与优选调度器
在 Kubernetes 1.14 版本之前,Scheduler 是基于预选(Predicates-Filtering)与优选(Priorities-Scoring)策略的调度器,如下图所示:
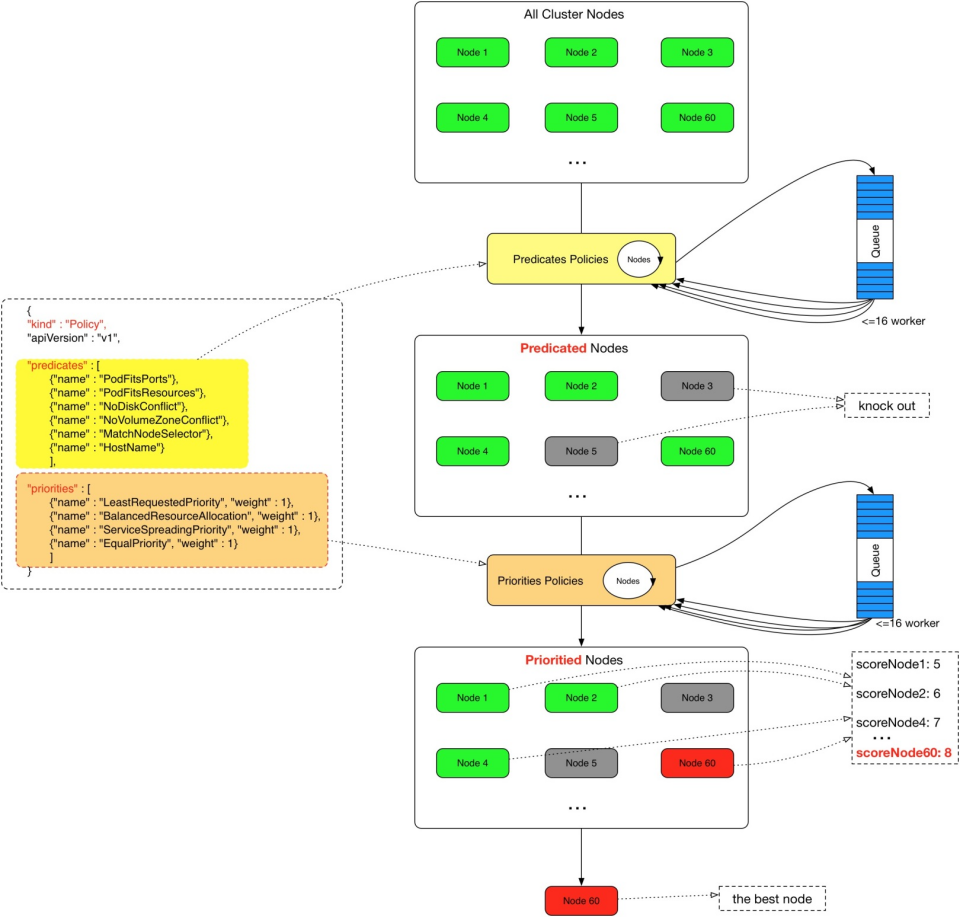
其中影响上述 Pod 调度到 Node 常见因素如下所示:
- podspec nodename
- podspec nodeselector
- Pod Priority(优先级) 与 Preemption(抢占)
- Pod Affinity(亲和性)与 Anti-affinity(反亲和性)
- Node Affinity(亲和性)与 Anti-affinity(反亲和性)
- Node Taints(污点)与 Tolerations(容忍度)
- Pod Disruption Budgets(PDB) 限制由于自愿中断(例如维护、升级、重新调度等)
扩展 Scheduler 调度器
一般来说,有4种扩展 Kubernetes 调度器的方法,如下所示:
| 扩展方式 | 优缺点 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| 修改 kube-scheduler 源码 | 不易维护 | |
| multiple schedulers | 可能会产生调度冲突问题,比如一个 scheduler bind 的时候实际资源已经被另一个 scheduler 已分配 | |
| extend scheduler | policy 文件可配置 Webhook,支持 Predicate、Priority、Bind、preemption 扩展点,实现简单 webhook 性能上会有一定损失,在有大量pod调度的时候会变慢,内部没有资源视图,需要自己获取 | gpushare-scheduler-extender |
| Scheduler Framework | Kubernetes v1.15 引入,extend scheduler即将被废弃,推荐 Scheduler Framework 插件形式扩展,方便和社区同步与原生 scheduler 联编,性能不会有问题 |
Scheduler Framework 调度器
整体架构
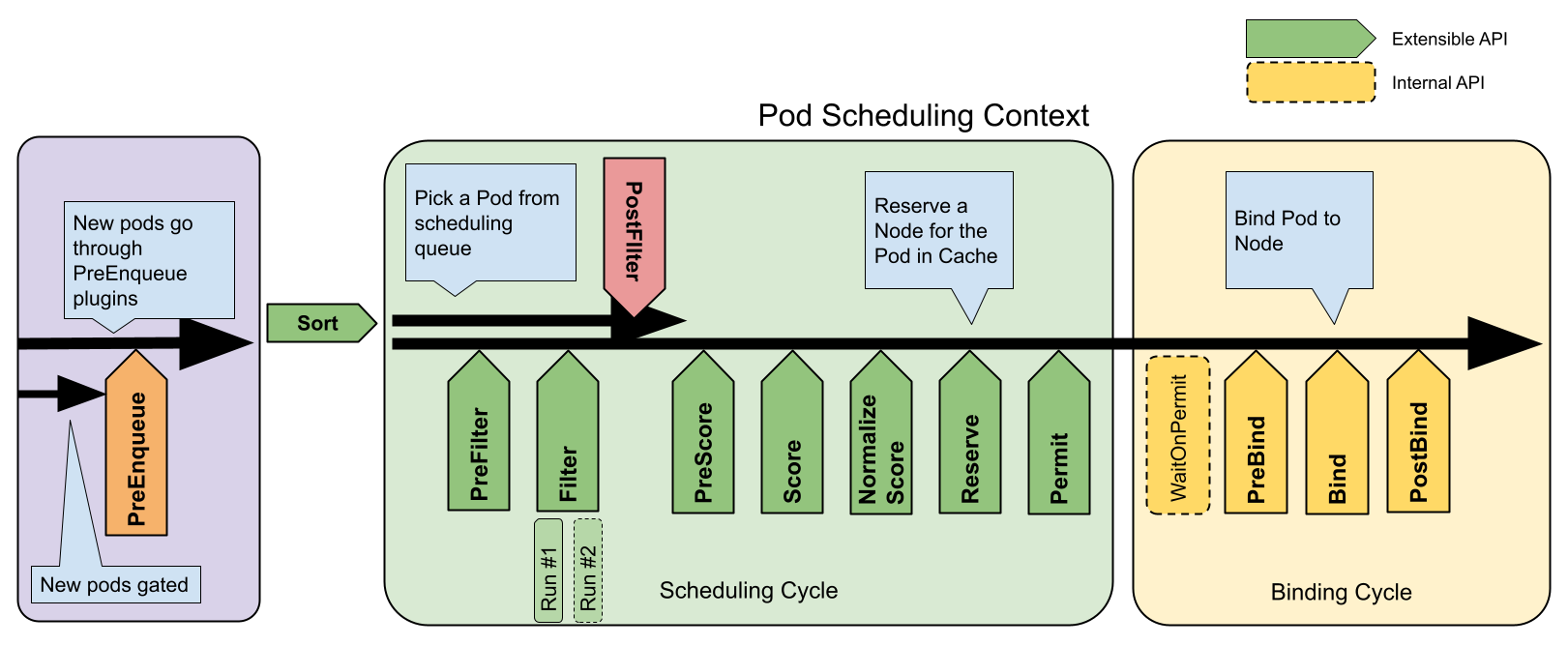
调度流程
Scheduler 分两个 cycle:Scheduling Cycle 和 Binding Cycle。在 Scheduling Cycle 中为了提升效率的一个重要原则就是 Pod、 Node 等信息从本地缓存中获取,而具体的实现原理就是先使用 list 获取所有 Node、Pod 的信息,然后再 watch 他们的变化更新本地缓存。在 Bind Cycle 中,会有两次外部 api 调用:调用 pv controller 绑定 pv 和调用 kube-apiserver 绑定 Node,api 调用是耗时的,所以将 bind 扩展点拆分出来,另起一个 go 协程进行 bind。
等待调度阶段
PreEnqueue
Pod 处于 ready for scheduling 的阶段。只有当所有 PreEnqueue 插件返回Success时,Pod 才允许进入活动队列。否则,它将被放置在内部无法调度的 Pod 列表中,并且不会获得Unschedulable状态。调度失败就不会进入调度队列,更不会进入调度流程。
QueueSort
排序扩展点,对调度队列(scheduling queue)内的 pod 进行排序,决定先调度哪些 pods,代码位于 kubernetes 的 pkg/scheduler/framework/interface.go 中:
// QueueSortPlugin is an interface that must be implemented by "QueueSort" plugins.
// These plugins are used to sort pods in the scheduling queue. Only one queue sort
// plugin may be enabled at a time.
type QueueSortPlugin interface {
Plugin
// Less are used to sort pods in the scheduling queue.
Less(*QueuedPodInfo, *QueuedPodInfo) bool
}
也就是只需要实现 Less 方法即可:
func Less(podInfo1, podInfo2 *framework.PodInfo) bool {
return GetPodPriority(podInfo1) > GetPodPriority(podInfo2)
}
sort 类型的扩展点只有一个,而且这个扩展点下面只能有一个插件可以运行,如果同时 enable 多个 sort 插件,scheduler 会退出。在 k8s 中,待调度的 Pod 会放在一个叫 activeQ 队列中,这个队列是一个基于堆实现的优先队列(priority queue)。因为可以对 Pod 设置优先级,将认为需要优先调度的 Pod 优先级调大,如果队列里有多个 Pod 需要调度,就会出现抢占现象,优先级高的 Pod 会移动到队列头部,scheduler 会优先取出这个 Pod 进行调度。那么这个优先级怎么设置呢?
- 如使用 k8s 默认 sort 插件,则可以给 Pod 设置 PriorityClass(创建 PriorityClass 资源并配置 deployment);如果所有 Pod 都没有设置 PriorityClass,那么会根据 Pod 创建的时间先后顺序进行调度。PriorityClass 和 Pod 创建时间是系统默认的排序依据。
- 实现自己的 sort 插件定制排序算法,根据该排序算法实现抢占,例如可以将包含特定标签的 Pod 移到队头。
调度阶段(Scheduling cycle)
filter 类型扩展点有3个:prefilter,filter,postfilter。各个扩展点有多个插件组成的插件集合根据 Pod 的配置共同过滤 Node。
preFilter 扩展点主要有两个作用,一是为后面的扩展点计算 Pod 的一些信息,例如 preFilter 阶段的 NodeResourcesFit 算法不会去判断节点合适与否,而是计算这个Pod需要多少资源,然后存储这个信息。Filter 扩展点的 NodeResourcesFit 插件会把之前算出来的资源拿出来做判断;另外一个作用就是过滤一些明显不符合要求的节点,这样可以减少后续扩展点插件一些无意义的计算。
filter 扩展点主要的作用就是根据各个插件定义的顺序依次执行,筛选出符合 Pod 的节点,这些插件会在 preFilter 后留下的每个 Node 上运行,如果能够通过所有插件,那么这个节点就留下来了。如果某个插件判断这个节点不符合,那么剩余的所有插件都不会对该节点做计算。
postFilter 扩展点只会在 filter 结束后没有任何 Node 符合 Pod 的情况下才会运行,否则这个扩展点会被跳过。这个扩展点在系统只有一个默认的插件,这个默认插件的作用遍历这个 Pod 所在的命名空间下面的所有 Pod,查找是否有可以被抢占的 Pod,如果有的话选出一个最合适的 Pod 然后 delete 掉这个Pod,并在待调度的 Pod 的 status 字段下面配置 nominateNode 为这个被抢占的 Pod。
- prefilter
- NodeResourcesFit
- NodePorts
- VolumeRestrictions
- PodTopologySpread
- InterPodAffinity
- VolumeBinding
- NodeAffinity
- filter
- NodeUnschedulable
- NodeName
- TaintToleration
- NodeAffinity
- NodePorts
- NodeResourcesFit
- VolumeRestrictions
- NodeVolumeLimits
- VolumeBinding
- VolumeZone
- PodTopologySpread
- InterPodAffinity
- postfilter
- DefaultPreemption
PreFilter
预过滤器插件应实现 PreFilter 函数,如果 PreFilter 返回错误,则调度周期将中止。Pre-filter 插件可以选择实现 PreFilterExtensions 接口。
// PreFilterPlugin is an interface that must be implemented by "PreFilter" plugins.
// These plugins are called at the beginning of the scheduling cycle.
type PreFilterPlugin interface {
Plugin
// PreFilter is called at the beginning of the scheduling cycle. All PreFilter
// plugins must return success or the pod will be rejected. PreFilter could optionally
// return a PreFilterResult to influence which nodes to evaluate downstream. This is useful
// for cases where it is possible to determine the subset of nodes to process in O(1) time.
PreFilter(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, p *v1.Pod) (*PreFilterResult, *Status)
// PreFilterExtensions returns a PreFilterExtensions interface if the plugin implements one,
// or nil if it does not. A Pre-filter plugin can provide extensions to incrementally
// modify its pre-processed info. The framework guarantees that the extensions
// AddPod/RemovePod will only be called after PreFilter, possibly on a cloned
// CycleState, and may call those functions more than once before calling
// Filter again on a specific node.
PreFilterExtensions() PreFilterExtensions
}
// PreFilterExtensions is an interface that is included in plugins that allow specifying
// callbacks to make incremental updates to its supposedly pre-calculated
// state.
type PreFilterExtensions interface {
// AddPod is called by the framework while trying to evaluate the impact
// of adding podToAdd to the node while scheduling podToSchedule.
AddPod(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, podToSchedule *v1.Pod, podInfoToAdd *PodInfo, nodeInfo *NodeInfo) *Status
// RemovePod is called by the framework while trying to evaluate the impact
// of removing podToRemove from the node while scheduling podToSchedule.
RemovePod(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, podToSchedule *v1.Pod, podInfoToRemove *PodInfo, nodeInfo *NodeInfo) *Status
}
- 输入
- podToSchedule *v1.Pod 是待调度的 pod;
- state 表示调度的上下文,可用于保存一些状态信息;
- 输出
- 只要有任何一个 plugin 返回失败,这个 pod 的调度就失败了;
- 所有已经注册的 PreFilter plugins 都成功之后,pod 才会进入到下一个环节;
Filter
可以过滤掉那些不满足要求的 Node,针对每个 Node,调度器会按配置顺序依次执行 filter plugins。 任何一个插件 返回失败,这个 node 就被排除;
// FilterPlugin is an interface for Filter plugins. These plugins are called at the
// filter extension point for filtering out hosts that cannot run a pod.
// This concept used to be called 'predicate' in the original scheduler.
// These plugins should return "Success", "Unschedulable" or "Error" in Status.code.
// However, the scheduler accepts other valid codes as well.
// Anything other than "Success" will lead to exclusion of the given host from running the pod.
type FilterPlugin interface {
Plugin
// Filter is called by the scheduling framework.
// All FilterPlugins should return "Success" to declare that
// the given node fits the pod. If Filter doesn't return "Success",
// it will return "Unschedulable", "UnschedulableAndUnresolvable" or "Error".
// For the node being evaluated, Filter plugins should look at the passed
// nodeInfo reference for this particular node's information (e.g., pods
// considered to be running on the node) instead of looking it up in the
// NodeInfoSnapshot because we don't guarantee that they will be the same.
// For example, during preemption, we may pass a copy of the original
// nodeInfo object that has some pods removed from it to evaluate the
// possibility of preempting them to schedule the target pod.
Filter(ctx , state *CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeInfo *NodeInfo) *Status
}
- 输入
- nodeInfo 是当前给定的 node 的信息,Filter() 程序判断这个 node 是否符合要求;
- 输出
- 放行或拒绝; 对于给定 node,如果所有 Filter plugins 都返回成功,该 node 才算通过筛选, 成为备选 node 之一。
PostFilter
如果 Filter 阶段之后,所有 nodes 都被筛掉了,一个都没剩,才会执行这个阶段;否则不会执行这个阶段的 plugins。
// PostFilterPlugin is an interface for "PostFilter" plugins. These plugins are called after a pod cannot be scheduled.
type PostFilterPlugin interface {
// A PostFilter plugin should return one of the following statuses:
// - Unschedulable: the plugin gets executed successfully but the pod cannot be made schedulable.
// - Success: the plugin gets executed successfully and the pod can be made schedulable.
// - Error: the plugin aborts due to some internal error.
//
// Informational plugins should be configured ahead of other ones, and always return Unschedulable status.
// Optionally, a non-nil PostFilterResult may be returned along with a Success status. For example,
// a preemption plugin may choose to return nominatedNodeName, so that framework can reuse that to update the
// preemptor pod's .spec.status.nominatedNodeName field.
PostFilter(ctx , state *CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, filteredNodeStatusMap NodeToStatusMap) (*PostFilterResult, *Status)
}
按 plugin 顺序依次执行,任何一个插件将 node 标记为Schedulable就算成功,不再执行剩下的 PostFilter plugins。典型的 PostFilter 实现是抢占,试图通过抢占其他 Pod 的资源使该 Pod 可以调度。
Score 类型的扩展点就是为上面 filter 扩展点筛选出来的所有 Node 进行打分,挑选出一个得分最高(最合适的),这个 Node 就是 Pod 要被调度上去的节点。这个类型的扩展有 preScore 和 score 两个,前者是为后者打分做前置准备的,preScore 的各个插件会计算一些信息供 score 使用,这个和 prefilter 比较类似。
PreScore
这些插件用于执行前置评分(pre-scoring)工作,即生成一个可共享状态供 Score 插件使用,如果 PreScore 插件返回错误,则调度周期将终止。
// PreScorePlugin is an interface for "PreScore" plugin. PreScore is an
// informational extension point. Plugins will be called with a list of nodes
// that passed the filtering phase. A plugin may use this data to update internal
// state or to generate logs/metrics.
type PreScorePlugin interface {
Plugin
// PreScore is called by the scheduling framework after a list of nodes
// passed the filtering phase. All prescore plugins must return success or
// the pod will be rejected
PreScore(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodes []*v1.Node) *Status
}
Score
这些插件用于对通过过滤阶段的节点进行排序。针对每个 node 依次调用 scoring plugin,得到一个分数(将有一个定义明确的整数范围,代表最小和最大分数)。在 normalize scoring 阶段,调度器将会把每个 scoring 扩展对具体某个节点的评分结果和该扩展的权重合并起来,作为最终评分结果。
// ScorePlugin is an interface that must be implemented by "Score" plugins to rank
// nodes that passed the filtering phase.
type ScorePlugin interface {
Plugin
// Score is called on each filtered node. It must return success and an integer
// indicating the rank of the node. All scoring plugins must return success or
// the pod will be rejected.
Score(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, p *v1.Pod, nodeName string) (int64, *Status)
// ScoreExtensions returns a ScoreExtensions interface if it implements one, or nil if does not.
ScoreExtensions() ScoreExtensions
}
NormalizeScore
在调度器对节点进行最终排序之前修改每个节点的评分结果,注册到该扩展点的扩展在被调用时,将使用同一个插件中的 score 扩展的评分结果作为参数,每个插件在每个调度周期调用一次。
// ScoreExtensions is an interface for Score extended functionality.
type ScoreExtensions interface {
// NormalizeScore is called for all node scores produced by the same plugin's "Score"
// method. A successful run of NormalizeScore will update the scores list and return
// a success status.
NormalizeScore(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, p *v1.Pod, scores NodeScoreList) *Status
}
Reserve
// ReservePlugin is an interface for plugins with Reserve and Unreserve// methods. These are meant to update the state of the plugin. This concept
// used to be called 'assume' in the original scheduler. These plugins should
// return only Success or Error in Status.code. However, the scheduler accepts
// other valid codes as well. Anything other than Success will lead to
// rejection of the pod.
type ReservePlugin interface {
// Reserve is called by the scheduling framework when the scheduler cache is
// updated. If this method returns a failed Status, the scheduler will call
// the Unreserve method for all enabled ReservePlugins.
Reserve(ctx , state *CycleState, p *v1.Pod, nodeName string) *Status
// Unreserve is called by the scheduling framework when a reserved pod was
// rejected, an error occurred during reservation of subsequent plugins, or
// in a later phase. The Unreserve method implementation must be idempotent
// and may be called by the scheduler even if the corresponding Reserve
// method for the same plugin was not called.
Unreserve(ctx , state *CycleState, p *v1.Pod, nodeName string)
}
Reserve是在调度程序实际将 Pod 绑定到 Node 之前发生的,它的存在是为了防止在调度程序等待绑定成功时发生资源竞争。如果一个 Reserve 方法调用失败,后面的插件就不会被执行,Reserve 阶段被认为失败。 如果所有插件的 Reserve 方法都成功了,Reserve 阶段就被认为是成功的, 剩下的调度周期和绑定周期就会被执行。
如果 Reserve 阶段或后续阶段失败了,则触发 Unreserve 阶段。 发生这种情况时,所有 Reserve 插件的 Unreserve 方法将按照 Reserve 方法调用的相反顺序执行。 这个阶段的存在是为了清理与保留的 Pod 相关的状态。
Permit
这是 scheduling cycle 的最后一个扩展点了,可以阻止或延迟将一个 pod binding 到 node。
// PermitPlugin is an interface that must be implemented by "Permit" plugins.
// These plugins are called before a pod is bound to a node.
type PermitPlugin interface {
// Permit is called before binding a pod (and before prebind plugins). Permit
// plugins are used to prevent or delay the binding of a Pod. A permit plugin
// must return success or wait with timeout duration, or the pod will be rejected.
// The pod will also be rejected if the wait timeout or the pod is rejected while
// waiting. Note that if the plugin returns "wait", the framework will wait only
// after running the remaining plugins given that no other plugin rejects the pod.
Permit(ctx , state *CycleState, p *v1.Pod, nodeName string) (*Status, time.Duration)
}
三种结果:
- approve:所有 Permit plugins 都 appove 之后,这个 pod 就进入下面的 binding 阶段;
- deny:任何一个 Permit plugin 拒绝后,就无法进入 binding 阶段,这会触发 Reserve plugins 的 Unreserve() 方法;
- wait (with a timeout):如果一个 Permit 插件返回 “wait”,则 Pod 将保持在一个内部的 “waiting” 的 Pod 列表,同时该 Pod 的绑定周期启动时即直接阻塞直到得到批准。如果超时发生,等待变成拒绝,并且 Pod 将返回调度队列,触发 Reserve plugins 的 Unreserve() 方法。
绑定阶段(binding cycle)
该类型扩展点有三个扩展点:preBind、bind 和 postBind。
preBind 扩展点有一个内置插件 VolumeBinding,这个插件会调用 pv controller 完成绑定操作,在前面的 reserve 也有同名插件,这个插件只是更新了本地缓存中的信息,没有实际做绑定。
bind 扩展点也只有一个默认的内置插件:DefaultBinder 将 Pod.Spec.nodeName 更新为选出来的那个 node,kubelet 监听到了 nodeName=Kubelet所在nodename,然后开始创建Pod(容器)。
PreBind
在将 pod 调度到一个 node 之前,先给这个 pod 在那台 node 上挂载一个 network volume。
// PreBindPlugin is an interface that must be implemented by "PreBind" plugins.
// These plugins are called before a pod being scheduled.
type PreBindPlugin interface {
// PreBind is called before binding a pod. All prebind plugins must return
// success or the pod will be rejected and won't be sent for binding.
PreBind(ctx , state *CycleState, p *v1.Pod, nodeName string) *Status
}
- 任何一个 PreBind plugin 失败,都会导致 pod 被拒绝,进入到 reserve plugins 的 Unreserve() 方法;
Bind
所有 PreBind 完成之后才会进入 Bind。
// Bind plugins are used to bind a pod to a Node.
type BindPlugin interface {
// Bind plugins will not be called until all pre-bind plugins have completed. Each
// bind plugin is called in the configured order. A bind plugin may choose whether
// or not to handle the given Pod. If a bind plugin chooses to handle a Pod, the
// remaining bind plugins are skipped. When a bind plugin does not handle a pod,
// it must return Skip in its Status code. If a bind plugin returns an Error, the
// pod is rejected and will not be bound.
Bind(ctx , state *CycleState, p *v1.Pod, nodeName string) *Status
}
- 所有 plugin 按配置顺序依次执行;
- 每个 plugin 可以选择是否要处理一个给定的 pod;如果选择处理,后面剩下的 plugins 会跳过,也就是最多只有一个 bind plugin 会执行;
PostBind
这是一个无法影响调度决策(没有返回值)。
- bind 成功的 pod 才会进入这个阶段;
- 作为 binding cycle 的最后一个阶段,一般是用来清理一些相关资源,如自身调度的中间态数据如缓存、状态等;
// PostBindPlugin is an interface that must be implemented by "PostBind" plugins.
// These plugins are called after a pod is successfully bound to a node.
type PostBindPlugin interface {
// PostBind is called after a pod is successfully bound. These plugins are informational.
// A common application of this extension point is for cleaning
// up. If a plugin needs to clean-up its state after a pod is scheduled and
// bound, PostBind is the extension point that it should register.
PostBind(ctx , state *Cycle
}